Monday, August 11, 2014
AP:Momentum Impulse J Problem Set
Key Concepts:
Friday, June 13, 2014
Period 9 Review Questions
The Exam is cumulative. Use you notebook as a guide to key ideas.
Here is a link to sample exam questions:
Here is a link to sample exam questions:
Wednesday, June 11, 2014
Phreshman Physics Click LINK BELOW
- Click link
- take notes
- Answer questions
- complete WS packet
Tuesday, June 10, 2014
Physics Final REVIEW QUESTIONS pd9
http://www.nysedregents.org/physics/
AP PHYSICS B WRAP UP
- FINAL PROJECTS DUE FRIDAY
- PHYSICS B STUDY GUIDES RETURNED
- TEXTBOOKS RETURNED w/COVER
- WILEY PLUS RESET PASSWORD
- LOG IN TO YOUR WILEYPLUS
- RESET THE PASSWORD TO PASSWORD
- IF YOU DO NOT YOU WILL BE BILLED FOR WILEY PLUS ACCESS
- $119.00
- You will not walk or receive a diploma until this obligation is cleared
- send registration info to jcrane@mainlandregional.net
Friday, June 6, 2014
Honors Physics P.9
- you can not save this and come back to it
- it is due by Sunday 6.8.14 @12 midnight
Thursday, June 5, 2014
Phreshman Physics
Newtons Laws Quarterly
- do not start this until after 3:00pm on 6.6.14
- you can not save this and come back to it
- it is due by Sunday 6.8.14 @12 midnight
AP PHYSICS FINAL PROJECT
Make an Electronic Charging Device
Create and Package an age appropriate activity for k-4 students
Include:
- Design
- Explain
- May be a infographic which explains the physics of the components in the charger
- Build
- Test
- Analysis
Create and Package an age appropriate activity for k-4 students
Include:
- Objectives and Standards
- Standards
- you can list standards other than science as they will apply
- math
- literacey
- science
- Materials List
- Instructions
- Short Youtube video with explanation or demonstration of activity
Tuesday, June 3, 2014
Thursday, May 29, 2014
Questato 1-7 tomorrow PHRESH PHYSICS
Please discuss any questions you have about the ws you should be able to
- draw FBD
- Write a stupid equation based on the FBD
- determine forces
- calculate accelerations
Wednesday, May 28, 2014
AP PHSYICS SONIC DISRUPTER TECHNOLOGY
RESEARCH AND POST LINKS TO INFORMATION ON THIS TECHNOLOGY.
Is it feasible to design a device similar to the one used in iron man?
How would it work?
How is it different than a flash-bang?
Is it feasible to design a device similar to the one used in iron man?
How would it work?
How is it different than a flash-bang?
Monday, May 12, 2014
▶ Newtons Dark Secrets - YouTube
▶ Newtons Dark Secrets - YouTube
Video: Newton's Dark Secrets | Watch NOVA Online | PBS Video
Answer: The following Questions on the BLOG and copy in your notebook.
For Extra Credit Create a Sketch or Portrait of Newton.
Please feel free to include supporting information and any additional thoughts.
Video: Newton's Dark Secrets | Watch NOVA Online | PBS Video
Answer: The following Questions on the BLOG and copy in your notebook.
For Extra Credit Create a Sketch or Portrait of Newton.
Please feel free to include supporting information and any additional thoughts.
Period
Newton’s Dark Secrets
1. Newton invented __________, and improved our understanding of ________
and _________.
2. Which famous scientist died in 1642, the same year Newton was born ?
3. When did Newton’s father die ?
4. Why did Newton dislike his mother ?
5. How many books did Newton have in his library ?
6. Why did he leave Cambridge and return home for awhile ?
7. Galileo dealt with average speed. Why did Newton invent a new field of
mathematics ?
8. Scientists before Newton had separated light with prisms, but what important
aspect of white light did he prove ?
9. What was the response of Cambridge students to Newton’s lectures ?
10. How was Newton’s telescope superior to Galileo’s ? Also, what did he use
that Galileo did not ?
11. What made Newton famous ?
12. What did the scientist Robert Hooke claim ?
13. Newton believed _______ _______ were encoded alchemic recipes.
14. Explain what Newton believed about Christ and God.
15. What was Newton trying to figure out with the 30 Bibles he owned ?
16. When Edmund Halley visited Newton to ask him about orbits, what shape did
Newton tell him orbits must have ?
17. When Newton published his 500 page book on motion, who once again tried
to take credit for the ideas ?
18. Why did some people criticize Newton’s Law of Gravity ?
19. What job did he take in London ?
20. What was Newton’s second book about ?
HONORS PERIOD 9
Week of 5/12/14
- A piece of unknown metal is heated in a flame until it begins to glow cherry red.
- Develop an experimental means to determine the temperature of the metal once removed from the flame
- Construct on a seperate piece of paper a well drawn & labeled info-graph using colored Pencils of Temperature vs. Heat for Ice transitioning from
- Ice @-60 to steam @ 1000oC
- Complete the Wave Diagram WS Provided by Substitute
- Draw all waves
- Record observations
- Draw any conclusions there are over 30 possible
- Amplitude,Frequency,Energy,Wavelength,Period,Speed
Pheshman Physics Week of 5/12
- FBD---.Force Diagrams or as we refer to them in Physics FREE BODY DIAGRAMS FBD not SBD
- Each assignment should be in your notebook. You do not need to copy the entire blog discussion just Key ideas (summary).
- I will be checking the Blog throughout the week.
- Calculate your Weight in Newton. Add to you Student information page.
- Weight is the force due to gravity (Newtons) see previous posts
- Calculate the weight in Newtons of 10 everyday Objects
- Complete FBD for 1-20 Discuss
- For each identify whether it accelerates or not.
- Draw the direction of the net force
- Complete Self Check Quiz put your answers in NOTEBOOK with TITLE FBD SCQ
- Complete FBD WS #2
- For each identify whether it accelerates or not.
- Draw the direction of the net force
- Watch Newtons Dark Secret
- Answer Questions on the Blog
- Use the idea of Force of gravity & mass to explain why all objects accelerate at 9.8m/s/s
- Post Online
Friday, May 9, 2014
Causes of Motion
Vocabulary:
- Force
- gravity,weight,normal,friction,tension,drag,lift,thrust
- Net
- Weight
- Mass
- Gravity
- =mxg
- Your weight calculated into newtons
- Constant velocity/Equilibrium
- a=0
- Fnet=0
- 1Newton
- The weight of an apple
- The weight of an apple iphone
Thursday, May 8, 2014
Wednesday, May 7, 2014
Physics is Driving me NUTZ!
Objectives
After studying the material of this chapter, you should be able to:1. Convert from joules to calories and kilocalories and vice versa.
2. Distinguish between the concepts of temperature and heat.
3. Explain what is meant by specific heat, latent heat of fusion, and latent heat of vaporization.
4. Apply the law of conservation of energy to problems involving calorimetry.
5. Distinguish the three ways that heat transfer occurs: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Peanut Lab This lab deals with heat and temperature and is teaching students about calories and the differences between calories and food calories. The students create a calorimeter and burn different foods to calculate the number of calories. Most students quickly learn that food calories are kilocalories. They also learn that potato chips, peanuts, and cheetos should all have warning labels "Keep away from flames: Fire Hazard".
http://imet.csus.edu/imet1/dave/portfolio/process.htm#Peanut Lab
Complete the Problem WS 1-10 and the Lab Form Below By Monday
Lab Form
Monday, May 5, 2014
Ariel Atom Phreshman
- Due next class!
- Watch Videos below
- Ariel atom 0-100-0 mph
- Calculate the change in position during the acceleration of the Atom.
- Calculate the change in position during the deceleration of the Atom.
- what other thing do you need to calculate first?
- please post with comments
Thursday, May 1, 2014
Phresman Practice Problems Due Monday
Do the problems in your notebook discuss the answers on the Blog. You can check your answers online to see if you get them correct but be sure to discuss the solutions.
- An airplane accelerates down a runway at 3.20 m/s2 for 32.8 s until is finally lifts off the ground. Determine the distance traveled before takeoff.
- A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly over a time of 5.21 seconds for a distance of 110 m. Determine the acceleration of the car.
- Upton Chuck is riding the Giant Drop at Great America. If Upton free falls for 2.60 seconds, what will be his final velocity and how far will he fall?
- A race car accelerates uniformly from 18.5 m/s to 46.1 m/s in 2.47 seconds. Determine the acceleration of the car and the distance traveled.
- A feather is dropped on the moon from a height of 1.40 meters. The acceleration of gravity on the moon is 1.67 m/s2. Determine the time for the feather to fall to the surface of the moon.
- Rocket-powered sleds are used to test the human response to acceleration. If a rocket-powered sled is accelerated to a speed of 444 m/s in 1.83 seconds, then what is the acceleration and what is the distance that the sled travels?
- A bike accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 7.10 m/s over a distance of 35.4 m. Determine the acceleration of the bike.
- An engineer is designing the runway for an airport. Of the planes that will use the airport, the lowest acceleration rate is likely to be 3 m/s2. The takeoff speed for this plane will be 65 m/s. Assuming this minimum acceleration, what is the minimum allowed length for the runway?
- A car traveling at 22.4 m/s skids to a stop in 2.55 s. Determine the skidding distance of the car (assume uniform acceleration).
- A kangaroo is capable of jumping to a height of 2.62 m. Determine the takeoff speed of the kangaroo.
Wednesday, April 30, 2014
Phresman Can't Jump!
Use the information you attained in class to determine your
If Mr. Crane has a vertical of .51M
Click Here you can compare your results to that of world class jumpers
- Hang time.
- Jump Velocity
- Hint:
If Mr. Crane has a vertical of .51M
- What is his hang time?
- What is his jump velocity?
- Is it possible to have a hang time of 1 second? Draw a diagram with all the important information to illustrate this phenomenon.
- Is it possible to increase your hang time by running first? Explain your reasoning. How can you test it?
Click Here you can compare your results to that of world class jumpers
Sunday, April 20, 2014
AP PHYSICS THERMODYNAMICS
Read the Chapters on Temperature and Heat
Try one of the following AP questions
Check Blog Frequently for updates
Do all posted work including your take home AP test
Print & Complete or copy into notebook
Do Problems 1-8
Resources:
Pencast 1
Pencast 2
Power Points
Do all posted work including your take home AP test
Print & Complete or copy into notebook
Do Problems 1-8
Resources:
Pencast 1
Pencast 2
Power Points
Objectives
After studying the material of this chapter, you should be able to:1. Convert a temperature given in degrees Fahrenheit to degrees Celsius and/or degrees Kelvin, and vice versa.
2. State the factors that cause the volume of a solid or liquid to change or the length of a solid to change. Also, solve word problems and determine the final length or volume.
3. Write the mathematical relationships that summarize Boyle's law, Charles law, Gay Lussac's law, and the ideal gas equation. Use these equations to solve word problems.
4. State in your own words Avogadro's hypothesis. State from memory the modern value of Avogadro's number.
5. State the postulates of the kinetic theory of gases.
6. Rewrite the ideal gas equation in terms of motion of the molecules of an ideal gas.
7. Explain what is meant by the term rms velocity.
8. Explain what is meant by Van der Waal's forces.
9. Given a phase diagram for water, determine the range of temperature and pressure at which water is a solid, liquid, or gas. Describe what is meant by the triple point of water and point out the triple point on a phase diagram.
10. Explain what is meant by sublimation and use a phase diagram to determine the range of temperatures and pressures for which the sublimation of water could occur.
11. Explain why evaporation from a liquid is related to the temperature of the liquid and the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the liquid.
12. Explain what is meant by vapor pressure and explain why vapor pressure is related to the temperature of the liquid and the boiling point of the liquid.
~13. Distinguish between relative humidity and absolute humidity and solve word problems related to relative humidity.
~14. Explain what is meant by diffusion and why diffusion is slower through a liquid than through a gas.
Friday, April 18, 2014
Period 4&7 Post Lab Questions HUMAN RXN TIME
You should be have computed your Avg reaction time.
- What are the units?
- What was your reaction distance? Why does it need to be in meters? Why is inches always a bad idea({you know who you are}?
- What is your % difference between the avg population? Avg=.21s
- Same formula as percent error Hint: Should be in your table of contents
- Hint: if its not... your Q4 notebook grade is not going to go well
- If Mr. Crane can check the bill which is 15 cm what is his reaction time?
- How does his reaction time compare to everyone else? How does everyone else compare to him? Support with numbers and calculations see #3
- Explain how this is possible?
- Finally- you should have a single page labeled in the back of your notebook and construct a well labeled table of personal information.
- create an entry for your reaction time and how it compares to the rest of the population
- you should include the date time it was calculated and initial it.
Thursday, April 17, 2014
Phresman Break Work
Complete all PUKE for classwork problems on worksheet "Chapter Problems"
- Check Blog Daily for the bonus question!
- Circle all information
- Box the unknown
- Draw a picture
- Make a list with labels of what the quantities represent (Known and Unknown)
- ex. a car starts from rest that means Vo=0 m/s
- Choose an equation and rearrange the variables so it solves for the Unknown
- Quiz first day back on Puking
Tuesday, April 15, 2014
Modern Marvels Energy
Option 1:
Either discuss the ideas on the blog and look into alternative "alternative" energy. Feel free to include links to any resources. Please post your name.
or complete the attached WS
Option 2:
Complete this WS for Thursday
Watch Video Here
Points of discussion :
cost, benefits, limitations technology any thing else you that comes to mind.
Either discuss the ideas on the blog and look into alternative "alternative" energy. Feel free to include links to any resources. Please post your name.
or complete the attached WS
Option 2:
Complete this WS for Thursday
Watch Video Here
Points of discussion :
cost, benefits, limitations technology any thing else you that comes to mind.
Friday, April 11, 2014
Bragn About Physics+
Thursday, April 10, 2014
Physics Makes Me PUKE
PWhat does PUKE stand for?
What should you do after reading the question? See Q#1 from class.
Complete 1-5
Remainder of notes for Baseball Guys
Monday, April 7, 2014
AP WAVES
Day 82 Notes from Class
6. State the conditions necessary for resonance. Give examples of instances where resonance is a) beneficial and b) destructive. Explain how damped harmonic motion can be achieved to prevent destructive resonance.
7. Distinguish between a longitudinal wave and a transverse wave and give examples of each type of wave.
8. Calculate the speed of longitudinal waves through liquids and solids and the speed of transverse waves in ropes and strings.
9. Calculate the energy transmitted by a wave, the power of a wave and the intensity of a wave, across a unit area A.
10. Describe wave reflection from a barrier, refraction as the wave travels from one medium into another, constructive and destructive interference as waves overlap, and diffraction of waves as they pass around an obstacle.
11. Explain how a standing wave can be produced in a string or rope and calculate the harmonic frequencies needed to produce standing waves in string instruments.
6. State the conditions necessary for resonance. Give examples of instances where resonance is a) beneficial and b) destructive. Explain how damped harmonic motion can be achieved to prevent destructive resonance.
7. Distinguish between a longitudinal wave and a transverse wave and give examples of each type of wave.
8. Calculate the speed of longitudinal waves through liquids and solids and the speed of transverse waves in ropes and strings.
9. Calculate the energy transmitted by a wave, the power of a wave and the intensity of a wave, across a unit area A.
10. Describe wave reflection from a barrier, refraction as the wave travels from one medium into another, constructive and destructive interference as waves overlap, and diffraction of waves as they pass around an obstacle.
11. Explain how a standing wave can be produced in a string or rope and calculate the harmonic frequencies needed to produce standing waves in string instruments.
Wednesday, April 2, 2014
Monday, March 31, 2014
AP Physics B Compton Scattering & Photo Electric Effect
- Day 79
- Use the photon theory and Compton's hypothesis to calculate the wavelength of a photon after it has been scattered as a result of a collision with an electron.
- Compton Scattering
- Notes
The Compton Effect is the quantum theory of the scattering of electromagnetic waves by
a charged particle in which a portion of the energy of the electromagnetic wave is given
to the charged particle in an elastic, relativistic collision. Compton scattering was
discovered in 1922 by Arthur H. Compton (1892-1962) while conducting research on the
scattering of x-rays by light elements. In 1922 he subsequently reported his experimental
and theoretical results and received the Nobel prize in 1927 for this discovery. His
theoretical explanation of what is now known as Compton scattering deviated from
classical theory and required the use of special relativity and quantum mechanics, both of
which were hardly understood at the time. When first reported, his results were
controversial, but his work quickly ...
Sunday, March 30, 2014
Losing My Marbles Lab P.9
SUBMIT LAB AND DATA HERE! DUE Friday!!!
.Conservation of momentum in 2-D
Momentum is conserved
.
.Conservation of momentum in 2-D
Momentum is conserved
- The total momentum before = the total momentum after
- Write the above idea down mathematically.
- Use your labeled and measured diagram to complete the expression i.e. What represents momentum? Why?
- this is the only physics idea in the lab
- Key Skills Required to complete the lab:
- Vectors
- Define F.O.R.
- Break into individual X&Y problems
- Find X&Y components
- Measurements
- Geometry
- Algebra
Whiteboard in real time:
http://www.twiddla.com/1562677
..
Friday, March 28, 2014
Phreshman Graphing motion 1-14
Discuss, post and answer questions here on the HW.
Link to the WS:
Read & Follow the directions carefully.
Help Drawing Slopes:
Drawing Slope and tangents
*** Here is a simulation to help you see and predict p/v/a graphs this is on the test this week.
--->>the above link requires java be installed and you may need to make an exception in your java control panel. see instructions
*** Here is a simulation to help you see and predict p/v/a graphs this is on the test this week.
--->>the above link requires java be installed and you may need to make an exception in your java control panel. see instructions
Wednesday, March 26, 2014
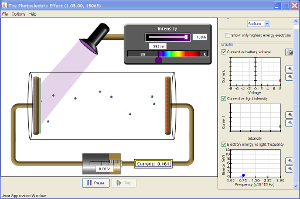
AP PHYSIC The Photo Electric Effect
Make Sure your Browser has Java running and enabled .
If the simulation does not run click here: Java
Objective use the same process described in class and determine the rules of photoelectric emmission
Identify related variables
Identify trends maxs and mins
A diagram should be in your notes as well
You may discuss on the Blog and work collaboratively
If the simulation does not run click here: Java
Objective use the same process described in class and determine the rules of photoelectric emmission
Identify related variables
Identify trends maxs and mins
A diagram should be in your notes as well
You may discuss on the Blog and work collaboratively
Friday, March 21, 2014
Pd4 Graph Stacks
Discuss questions and ideas here. For questions 4-6.
AP Physics Test Tue Circuits and Electricity
Test Review Circuits
Test will include some electrostatic principles.
Test will include some electrostatic principles.
Tuesday, March 18, 2014
P.9 Momentum
Objectives
After studying the material of this chapter, you should be able to:1. Define linear momentum and write the mathematical formula for linear momentum from memory.
2. Distinguish between the unit of force and momentum.
3. Write Newton's Second Law of Motion in terms of momentum.
4. Define impulse and write the equation that connects impulse and momentum.
5. State the Law of Conservation of Momentum and write, in vector form, the law for a system involving two or more point masses.
6. Distinguish between a perfectly elastic collision and a completely inelastic collision.
7. Apply the laws of conservation of momentum and energy to problems involving collisions between two point masses.
Day 72
Momentum Makes me want to PUKE
Develop Strategies & Practice solving simple momentum and Impulse questions
Recitation and questions
HW
Complete 5 of the practice problems
Day 71
Summarize Newtons Cradle Activity
Demonstration Impulse & A Change in Momentum
"Egg-citing Physics"
Explain how the same impulse can yield different results and why?
Day 70
Make Observations about Newon's Cradle
Guided Demonstration/Lab
Define Determine Differentiate Momentum and Impulse
Monday, March 17, 2014
AP P2
Complete & Discuss on the Blog
The 1995 question
Questions
Methods
Solutions
Also for the circuit with a capacitor (2000) look at your equation sheet. Easy Peasy.
AP P2
Complete the Question below.
•
 In the circuit shown below, A, B,C, and D are identical light bulbs. Assume that the battery maintains a constant potential difference between its terminals (i.e., the internal resistance of the battery is assumed to be negligible) and the resistance of each light bulb remains constant.
In the circuit shown below, A, B,C, and D are identical light bulbs. Assume that the battery maintains a constant potential difference between its terminals (i.e., the internal resistance of the battery is assumed to be negligible) and the resistance of each light bulb remains constant.Draw a diagram of the circuit in the box below, using the following symbols to represent the components in your diagram. Label the resistors A,B, C, and D to refer to the corresponding light bulbs.
->List the bulbs in order of their brightness, from brightest to least bright. If any two or more bulbs have the same brightness, state which ones. Justify your answer.
->Bulb D is then removed from its socket.
.
Describe the change in the brightness, if any, of bulb A when bulb D is removed form its socket. Justify your answer.->Describe the change in the brightness, if any, of bulb B when bulb D is removed from its socket. Justify you answer.
B. List the bulbs in order of their brightness, from brightest to least bright. If any two or more bulbs have the same brightness, state which ones. Justify your answer.
.
Describe the change in the brightness, if any, of bulb B when bulb D is removed from its socket. Justify you answer.
Bulb B becomes brighter.
It was receiving the least amount of current since D was an alternate pathway for the current. With D gone all the current must go through B, which is in series now. More current means B will be brighter.
Sunday, March 16, 2014
All Ramped up period 4 only
Some hints:
Why is this graph signicant to the lab?
How is this different than any other WB?
What is the idea that explains the difference?
Sorry did this Friday & it said it posted!
Monday, March 10, 2014
Fc Right Round The Lab
Due 3.14.14
Day 67,68
NJ STATE STANDARD 5.1
NJ STANDARD5.2 E
Submit Your Data & calculations here
Objective: Develop record and safely execute a lab that will prove Fc=(mv^2)/r
record all data in notebook using charts and or tables.
Day 67,68
NJ STATE STANDARD 5.1
NJ STANDARD5.2 E
Submit Your Data & calculations here
Objective: Develop record and safely execute a lab that will prove Fc=(mv^2)/r
record all data in notebook using charts and or tables.
- Wear Goggles while labs are being performed
- You may discuss any ideas questions or concerns on the blog.
- Groups of 2
- You are responsible for your own calculations!!! you have been warned.
Friday, February 28, 2014
Electric Circuits & Ohms Law
***** FREE RESOURCE--->5Easy Steps to Get A 5 on the AP Physics Exam
After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to:
1. Explain how a simple battery can produce an electrical current.
2. Define current, ampere, emf, voltage, resistance, resistivity, and temperature coefficient of resistance.
4. Distinguish between a) conventional current and electron current and b) direct current and alternating current.
5. Know the symbols used to represent a source of emf, resistor, voltmeter, and ammeter and how to interpret a simple circuit diagram.
6. Given the length, cross sectional area, resistivity, and temperature coefficient of resistance, determine a wire's resistance at room temperature and some higher or lower temperature.
7. Solve simple dc circuit problems using Ohm's law.
8. Use the equations for electric power to determine the power and energy dissipated in a resistor and calculate the cost of this energy to the consumer.
1. Determine the equivalent resistance of resistors arranged in series or in parallel or the equivalent resistance of a series parallel combination.
2. Use Ohm's law and Kirchhoff's rules to determine the current through each resistor and the voltage drop across each resistor in a single loop or multiloop dc circuit.
3. Distinguish between the emf and the terminal voltage of a battery and calculate the terminal voltage given the emf, internal resistance of the battery, and external resistance in the circuit.
4. Determine the equivalent capacitance of capacitors arranged in series or in parallel or the equivalent capacitance of a series parallel combination.
5. Determine the charge on each capacitor and the voltage drop across each capacitor in a circuit where capacitors are arranged in series, parallel, or a series parallel combination.
6. Calculate the time constant of an RC circuit.
Day 67
Introduction to Basic Circuits & Diagrams.
Notes: Circuit Symbology
Drawing Circuit Diagram
Ohm's Law Lab
Day 69
1. Explain how a simple battery can produce an electrical current.
2. Define current, ampere, emf, voltage, resistance, resistivity, and temperature coefficient of resistance.
4. Distinguish between a) conventional current and electron current and b) direct current and alternating current.
5. Know the symbols used to represent a source of emf, resistor, voltmeter, and ammeter and how to interpret a simple circuit diagram.
6. Given the length, cross sectional area, resistivity, and temperature coefficient of resistance, determine a wire's resistance at room temperature and some higher or lower temperature.
7. Solve simple dc circuit problems using Ohm's law.
8. Use the equations for electric power to determine the power and energy dissipated in a resistor and calculate the cost of this energy to the consumer.
1. Determine the equivalent resistance of resistors arranged in series or in parallel or the equivalent resistance of a series parallel combination.
2. Use Ohm's law and Kirchhoff's rules to determine the current through each resistor and the voltage drop across each resistor in a single loop or multiloop dc circuit.
3. Distinguish between the emf and the terminal voltage of a battery and calculate the terminal voltage given the emf, internal resistance of the battery, and external resistance in the circuit.
4. Determine the equivalent capacitance of capacitors arranged in series or in parallel or the equivalent capacitance of a series parallel combination.
5. Determine the charge on each capacitor and the voltage drop across each capacitor in a circuit where capacitors are arranged in series, parallel, or a series parallel combination.
6. Calculate the time constant of an RC circuit.
Day 67
Introduction to Basic Circuits & Diagrams.
Notes: Circuit Symbology
Drawing Circuit Diagram
- Battery Voltage Source
- Wires
- Resistors and Bulbs
- Switches
Ohm's Law Lab
Day 69
Ohm's Law
Conclusions
Day 70
Easter Bunny Rules
Recitation Circuits WS
HW complete circuits WS
Practice Quiz:
http://www.indiabix.com/electronics/series-circuits/Objectives
Day 71
Circuits Quest con Queso
Day 72
Hotdog Hotdog hot digity dog
Magnetic Fields Continued
Day 60
Practice of RHR and its applications of right hand rule
Online practice questions
http://www.allenisd.org/cms/lib/TX01001197/Centricity/Domain/1840/Magnetism/Hot%20Potato%20Magnetism%20Graphics/Right_hand_rule_practice_1_jb.htm
Day 61
Forces between current carrying wire notes diagrams and discussion
Yamato 1 magnetohydrodrive-> notes and discussion
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetohydrodynamic_drive
Day 62
Induced EMF
As it pertains to RHR. Wire sections and loops entering magnetic fields
3 cases will be discussed and students will simplify analyze and apply RHR to and between case to explain the resulting current of a wire in a magnetic field.
Day 63
Quest on the direction and application of the RHR " Macarena effect quiz"
Worlds simplistic motor student will set up and observe the operation of a simple motor consisting of a coil a battery and a magnet.
Students will make observations
Explain the purpose for each component and step in order to produce the desired effect
Relate back to RHR
Day 64
Summarize key ideas to date-
Discussion and Summary of key concepts of simple electric motor.
Phase/ flux/ RHR will be explained in context. The ultimate goals is to provide the construct example for the functionality of emf to be used in future study of rail guns and emf.
Notes mass spectrograph-
AP2000 b7 student will analyze and explain both qualitatively and quantitatively the function of the device.
Day 65
Choose Any 2 EMAG problems form the AP EXAMS
Develop Solutions and Solve.
Day66
WhiteBoard of problems from previous day.
Day 67
Intorduction to Basic Circuits & Diagrams.
Battery Voltage SOurce
Wires
Resistors and Bulbs
Switches
Practice of RHR and its applications of right hand rule
Online practice questions
http://www.allenisd.org/cms/lib/TX01001197/Centricity/Domain/1840/Magnetism/Hot%20Potato%20Magnetism%20Graphics/Right_hand_rule_practice_1_jb.htm
Day 61
Forces between current carrying wire notes diagrams and discussion
Yamato 1 magnetohydrodrive-> notes and discussion
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetohydrodynamic_drive
Day 62
Induced EMF
As it pertains to RHR. Wire sections and loops entering magnetic fields
3 cases will be discussed and students will simplify analyze and apply RHR to and between case to explain the resulting current of a wire in a magnetic field.
Day 63
Quest on the direction and application of the RHR " Macarena effect quiz"
Worlds simplistic motor student will set up and observe the operation of a simple motor consisting of a coil a battery and a magnet.
Students will make observations
Explain the purpose for each component and step in order to produce the desired effect
Relate back to RHR
Day 64
Summarize key ideas to date-
Discussion and Summary of key concepts of simple electric motor.
Phase/ flux/ RHR will be explained in context. The ultimate goals is to provide the construct example for the functionality of emf to be used in future study of rail guns and emf.
Notes mass spectrograph-
AP2000 b7 student will analyze and explain both qualitatively and quantitatively the function of the device.
Day 65
Choose Any 2 EMAG problems form the AP EXAMS
Develop Solutions and Solve.
Day66
WhiteBoard of problems from previous day.
Day 67
Intorduction to Basic Circuits & Diagrams.
Battery Voltage SOurce
Wires
Resistors and Bulbs
Switches
Saturday, February 22, 2014
Centripetal Force & Gravitation
OK. So if you check the blog and you are able to finish your calculation of the mass of the sun, you only need to do 2 other problems from the ws. not the entire thing.
How do you know what the correct answers is ? Easy ~2X10^30Kg
Here is a link to the text if you need help "CICK HERE"

1. Calculate the centripetal acceleration of a point mass in uniform circular motion given the radius of the circle and either the linear speed or the period of the motion.
2. Identify the force that is the cause of the centripetal acceleration and determine the direction of the acceleration vector.
3. Use Newton's laws of motion and the concept of centripetal acceleration to solve word problems.
4. Distinguish between centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration.
5. State the relationship between the period of the motion and the frequency of rotation and express this relationship using a mathematical equation.
6. Write the equation for Newton's universal law of gravitation and explain the meaning of each symbol in the equation.
7. Determine the magnitude and direction of the gravitational field strength (g) at a distance r from a body of mass m.
8. Use Newton's second law of motion, the universal law of gravitation, and the concept of centripetal acceleration to solve problems involving the orbital motion of satellites.
9. Explain the "apparent" weightlessness of an astronaut in orbit.
10. State from memory Kepler's laws of planetary motion. NOT! Derive ideas and formulas based on DUMB IDEAS Like Fnet=Fc=FG
11. Use Kepler's third law to solve word problems involving planetary motion.
12. Use Newton's second law of motion, the universal law of gravitation, and the concept of centripetal acceleration to derive Kepler's third law.
13. Solve word problems related to Kepler's third law.
14. Identify the four forces that exist in nature. ALL DAY EVERY DAY
Practice PROBLEMS WS 7H
How do you know what the correct answers is ? Easy ~2X10^30Kg
Here is a link to the text if you need help "CICK HERE"

1. Calculate the centripetal acceleration of a point mass in uniform circular motion given the radius of the circle and either the linear speed or the period of the motion.
2. Identify the force that is the cause of the centripetal acceleration and determine the direction of the acceleration vector.
3. Use Newton's laws of motion and the concept of centripetal acceleration to solve word problems.
4. Distinguish between centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration.
5. State the relationship between the period of the motion and the frequency of rotation and express this relationship using a mathematical equation.
6. Write the equation for Newton's universal law of gravitation and explain the meaning of each symbol in the equation.
7. Determine the magnitude and direction of the gravitational field strength (g) at a distance r from a body of mass m.
8. Use Newton's second law of motion, the universal law of gravitation, and the concept of centripetal acceleration to solve problems involving the orbital motion of satellites.
9. Explain the "apparent" weightlessness of an astronaut in orbit.
10. State from memory Kepler's laws of planetary motion. NOT! Derive ideas and formulas based on DUMB IDEAS Like Fnet=Fc=FG
11. Use Kepler's third law to solve word problems involving planetary motion.
12. Use Newton's second law of motion, the universal law of gravitation, and the concept of centripetal acceleration to derive Kepler's third law.
13. Solve word problems related to Kepler's third law.
14. Identify the four forces that exist in nature. ALL DAY EVERY DAY
Practice PROBLEMS WS 7H
Monday, February 10, 2014
Magnetism
Every AP Magnetism Problem to Date
Objectives
After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to:1. Draw the magnetic field pattern produced by iron filings sprinkled on paper placed over different arrangements of bar magnets.
2. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic field produced by both a long straight current-carrying wire and a current loop. Use the right hand rule to determine the direction of the magnetic field produced by the current.
3. Explain what is meant by ferromagnetism, including the concept of domains and the *Curie temperature.
4. State the conventions adopted to represent the direction of a magnetic field, the current in a current-carrying wire and the direction of motion of a charged particle moving through a magnetic field.
5. Apply the right hand rule to determine the direction of the force on either a charged particle traveling through a magnetic field or a current-carrying wire placed in a magnetic field.
6. Determine the torque on a current loop arranged in a magnetic field and explain galvanometer movement.
7. Explain how a mass spectrograph can be used to determine the mass of an ion and how it can be used to separate isotopes of the same element.
Day 56
Electormagnetism:
SS:5.1
Coil Compass Battery & Wire Ohm my!
- Investigate and make/write observations about interactions between the components.
- model simplification ex. Milikan oil drop
Day 58
- Return Potential Potential Difference Quest discuss and revise errors in reasoning
- Introduction to the Right Hand Rule and Force
*Every AP Magnetism Problem to Date
Day 60
Practice of RHR and its applications of right hand rule
Online practice questions
http://www.allenisd.org/cms/lib/TX01001197/Centricity/Domain/1840/Magnetism/Hot%20Potato%20Magnetism%20Graphics/Right_hand_rule_practice_1_jb.htm
Day 61
Forces between current carrying wire notes diagrams and discussion
Yamato 1 magnetohydrodrive-> notes and discussion
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetohydrodynamic_drive
Day 62
Induced EMF
As it pertains to RHR. Wire sections and loops entering magnetic fields
3 cases will be discussed and students will simplify analyze and apply RHR to and between case to explain the resulting current of a wire in a magnetic field.
Day 63
Quest on the direction and application of the RHR " Macarena effect quiz"
Worlds simplistic motor student will set up and observe the operation of a simple motor consisting of a coil a battery and a magnet.
Students will make observations
Explain the purpose for each component and step in order to produce the desired effect
Relate back to RHR
Day 64
Summarize key ideas to date-
Discussion and Summary of key concepts of simple electric motor.
Phase/ flux/ RHR will be explained in context. The ultimate goals is to provide the construct example for the functionality of emf to be used in future study of rail guns and emf.
Notes mass spectrograph-
AP2000 b7 student will analyze and explain both qualitatively and quantitatively the function of the device.
Wednesday, February 5, 2014
Phershman PHYSICS
2/22/14
Some people asked about reading Motion Maps
2/7/14 HW WS Click Here! Complete 4&5 you may discuss
Objectives:
1.1 A CVPM I know the difference between vector and scalar quantities.
1.2 A CVPM I know the difference between position, distance, and displacement.
1.3 A CVPM I can interpret/draw motion maps for objects moving with constant velocity.
1.4 A CVPM I can interpret/draw the position vs. time graph for an object moving with constant velocity.
1.5 A CVPM I can interpret/draw the velocity vs. time graph for an object moving with constant velocity.
1.6 B CVPM I can draw the corresponding position-vs-time graph given a velocity-vs-time graph.
1.7 B CVPM I can solve problems involving average speed and average velocity.
Watch Video
Draw a motion map for both the squirrel and man.
Sketch a graph of their motions be sure to include all key points.
Some people asked about reading Motion Maps
- How to Read a Motion Map ClickHere
- Key Ideas for Motion Postion vs. time
- KEY IDEAS
2/7/14 HW WS Click Here! Complete 4&5 you may discuss
Objectives:
Honors Physics
Constant Velocity Particle Model1.1 A CVPM I know the difference between vector and scalar quantities.
1.2 A CVPM I know the difference between position, distance, and displacement.
1.3 A CVPM I can interpret/draw motion maps for objects moving with constant velocity.
1.4 A CVPM I can interpret/draw the position vs. time graph for an object moving with constant velocity.
1.5 A CVPM I can interpret/draw the velocity vs. time graph for an object moving with constant velocity.
1.6 B CVPM I can draw the corresponding position-vs-time graph given a velocity-vs-time graph.
1.7 B CVPM I can solve problems involving average speed and average velocity.
Watch Video
Draw a motion map for both the squirrel and man.
Sketch a graph of their motions be sure to include all key points.
Sunday, February 2, 2014
Electric Potential and Potential Difference
"Voltage"
State Standard 5.2 A-E
Objectives
After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to:1. Write from memory the definitions of electric potential, and electric potential difference.
2. Distinguish between electric potential, electric potential energy, and electric potential difference.
3. Draw the electric field pattern and equipotential line pattern which exist between charged objects.
4. Determine the magnitude of the potential at a point a known distance from a point charge or an arrangement of point charges.
5. State the relationship between electric potential and electric field and determine the potential difference between two points a fixed distance apart in a region where the electric field is uniform.
6. Determine the kinetic energy in both joules and electron volts of a charged particle which is accelerated through a given potential difference.
7. Explain what is meant by an electric dipole and determine the magnitude of the electric dipole moment between two point charges.
8. Given the dimensions, distance between the plates, and the dielectric constant of the material between the plates, determine the magnitude of the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.
9. Given the capacitance, the dielectric constant, and either the potential difference or the charge stored on the plates of a parallel plate capacitor, determine the energy and the energy density stored in the capacitor.
- Day 53
- 1985 B2 Complete Practice Problem after derivation of V=kq/r
- magnetic abstraction to help answer e.
- students hold one magnet and move other in the field make analogies between the 2 situations
- Group Work Graded assignment 1989 #2
- HW:
- Day 54
- White Board & Discuss Previous HW
- Day 55 Test Fields Potential and Review Question
State Standard 5.2 A-E
Student Learning Objectives
- To observe the experimental evidence for electromagnetic induction.
- To understand the circumstances under which changing magnetic fields lead to induced currents.
- To understand how the movement of a conductor through a magnetic field leads to a motional emf.
- To understand and use Lenz’s law for induced currents.
- To use Lenz’s law and Faraday’s law to determine the direction and size of induced currents.
- To understand basic applications of electromagnetic induction to technology.
- Day 56
- Introduction to Electromagnetic Induction
- Discovery Experimentation activity
- 9v Battery/compass/ coil of wire
- Identify variables and qualitative interactions
- Defn relationships and quantities
- relate equations
- sample problem full abstraction
- HW: Read Electromagnetic Induction
Thursday, January 30, 2014
Honor Physics Period 9

State Standard 5.2.E Forces
- Engineering
- Objectives:
- calculate all of the forces for objects
on any surface that is not horizontal. - calculate the acceleration of these
objects and apply motion equations. - Skills Required
- FBD->Free Body Diagrams
- Finding Vector Componants
- Sum of the Forces
- PUKES
- Algebra
- Steps for Solving "you need to memorize this"
- 1) Draw a free-body diagram for the object (the normal force is perpendicular to the plane; the friction force acts along the plane, opposite the velocity)
- 2) break vectors into components, where the parallel component of weight is mg(sin θ);
- 3) write Newton's second law for parallel and perpendicular components; and
- 4) solve the equations for whatever the problem asks for.
- Week of 2/3/14
- Day 54
- Check HW
- Review HW FBD WS Whiteboarding corrections and discussion
- Practice: Drawing FBD and writing Sum of the Forces
- Day 55
- Class Clicker Quiz
- Day 56
- WB remaning problems
- Day 57
- Mastery Learning (Complete all questions w/ FBD/SUM of the Forces/PUKES
- Sample Problem #1
- WS 1-8 with solved example #1
- Students may ask questions and work together to complete
- Week of 2/10/14
- Day 58
- Mastery Learning (Complete all questions w/ FBD/SUM of the Forces/PUKES
- Students may ask questions collaborate and work together to complete
- Day 59
- Mastery Learning (Complete all questions w/ FBD/SUM of the Forces/PUKES
- Students may ask questions collaborate and work together to complete
- Day 60
- Mastery Learning (Complete all questions w/ FBD/SUM of the Forces/PUKES
- Students may ask questions collaborate and work together to complete
- PROBLEMS DUE @ END OF CLASS THURSDAY!!!!
Saturday, January 18, 2014
Wednesday, January 15, 2014
Period 9 MID TERM REVIEW
Regents Test
Extra Credit T/F Review Test
You will be required to complete a scan-tron "No whining!"
The idea of forces is on the exam... Most importantly that they are vectors and behave as such.
The total FORCE= Net Force=(Fnet)=ma
Or simply Fnet=ma
There are only to possibilities when it comes to Fnet:
They add up to zero (equilibrium)
Or they don't and the object accelerates.
Here are some sample questions:
https://www.box.com/s/22v28qs6dx7uosh4iw8z
Answers:
https://www.box.com/s/8j5bo5gdrwvsr2nwcvm2
You are permitted to bring one side 8.5x11 inch paper with hand written equation sheet you may include diagrams but no notes.
There is no curve!!!
It is a Pre determined standard.
80 correct = 100
70=90
60=80
50=70
48=68
Extra Credit T/F Review Test
You will be required to complete a scan-tron "No whining!"
The idea of forces is on the exam... Most importantly that they are vectors and behave as such.
The total FORCE= Net Force=(Fnet)=ma
Or simply Fnet=ma
There are only to possibilities when it comes to Fnet:
They add up to zero (equilibrium)
Or they don't and the object accelerates.
Here are some sample questions:
https://www.box.com/s/22v28qs6dx7uosh4iw8z
Answers:
https://www.box.com/s/8j5bo5gdrwvsr2nwcvm2
You are permitted to bring one side 8.5x11 inch paper with hand written equation sheet you may include diagrams but no notes.
There is no curve!!!
It is a Pre determined standard.
80 correct = 100
70=90
60=80
50=70
48=68
Phreshman Physics MIDTERM REVIEW
All or some of these topics may be on the exam.
What is Physics?
Observations:
Subjective Objective
Measurements:
Prefixes
Measuring
Fundamental & Derived units
Factor Label
Sig Figs
Labs:
Easy as PI
Not as Easy as PI
Physics Bugs me!
Graphing:
Graph:20 Pts
Graph
Scale 2 pts
Title 2 pts
BLOF 2pts
Axis Label 2pts
Slope 4pts
intercept 2pts
Identification 2 pts
Equation in terms 4 pts
Parent Graphs:
4 from class
Units
What is Physics?
Observations:
Subjective Objective
Measurements:
Prefixes
Measuring
Fundamental & Derived units
Factor Label
Sig Figs
Labs:
Easy as PI
Not as Easy as PI
Physics Bugs me!
Graphing:
Graph:20 Pts
Graph
Scale 2 pts
Title 2 pts
BLOF 2pts
Axis Label 2pts
Slope 4pts
intercept 2pts
Identification 2 pts
Equation in terms 4 pts
Parent Graphs:
4 from class
Units
Tuesday, January 14, 2014
Honors Physics
- Force Diagrams
- Complete the diagrams 1-10.
- If you cant not print the WS sketch in your notebooks.
- All diagrams should be labeled.
- Post any questions or issues along with the Q#.
Sunday, January 12, 2014
Friday, January 10, 2014
Eletric Field Mapping Lab
- Due tomorrow Tues 1.14.14
- Electric Field Maps
- Colorized
- observations
- interpretations
- Post Lab Question "Click Here"
- on a separate piece of printer paper NDPS
- Print or sketch the picture/question
- answer the questions
- http://groups.physics.northwestern.edu/lab/DOWNLOAD/equipotential.pdf
Need Ideas
Infographics
Assignments:
Fileds Potential Work
Midterm Strategies MC Strategies
How to Eliminate Choices:
- What UNIT should the answer be in? Especially for those questions with no numbers. Look at the arrangements of the variables to find which choices are in the correct units (dimensional analysis)
- Should the answer be larger or smaller than a given value in the problem? (increase/decrease/relationship problems)
- For graphs, think about probable shapes and slopes. Where the line goes to zero is often a good indicator of correct or incorrect choices.
- For those questions that read “Which of the following…” Be extremely careful of the word NOT and be sure to read ALL the choices before picking one. Many mistakes are made when a student picks choice A after reading it and never even gets to B through E.
- Predict the sign of your answer (+/–) to eliminate choices
- Predict the possible directions (for currents, vectors, etc.) to eliminate choices
taken from PGP physics
How to Eliminate Choices:
- What UNIT should the answer be in? Especially for those questions with
are in the correct units (dimensional analysis)
- Should the answer be larger or smaller than a given value in the problem?
(increase/decrease/relationship problems)
- For graphs, think about probable shapes and slopes. Where the line goes to zero is often a
- For those questions that read “Which of the following…” Be extremely
careful of the word NOT and be sure to read ALL the choices before picking
one.
- Predict the sign of your answer (+/–) to eliminate choices
- Predict the possible directions (for currents, vectors, etc.) to
- Many mistakes are made when a student picks choice A after reading it and never even gets to B through E.
eliminate choices
Friday, January 3, 2014
HONORS PHYSICS P9 2 Dimensional Motion
Key Strategies:
http://go.hrw.com/resources/go_sc/phy/HF2PW03D.PDF
- divide the problem into 2 linear motion problems using PUKE
- one for the x and 1 for the y
- Time for the x&y are the same {the motions are occurring independently and simultaneously}
- Solve for time using PUKE"S" in either the x or y and apply it to the other direction.
- You are not learning anything new
http://go.hrw.com/resources/go_sc/phy/HF2PW03D.PDF
AP PHYSICS B 1&2 Mechanical Universe VIDEO
Use the Video Links Below to view and discuss. There are questions as a guide though you shouldn't need them. Discuss on Blog.
Best if viewed with Firefox: Popups must be enabled.
Note:*if the titles don't appear find the videos in the directory below the page that appears.
| 28. Static Electricity | Worksheet 28 | Video Link 28 | |
| 29. The Electric Field | Worksheet 29 | Video Link 29 |
Thursday, January 2, 2014
AP ELECTRICTY Part 1 Electrostatics
Objectives
After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to:1. State from memory the magnitude and sign of the charge on an electron and proton and also state the mass of each particle.
2. Apply Coulomb's law to determine the magnitude of the electrical force between point charges separated by a distance r and state whether the force will be one of attraction or repulsion.
3. State from memory the law of conservation of charge.
4. Distinguish between an insulator, a conductor, and a semi conductor and give examples of each.
5. Explain the concept of electric field and determine the resultant electric field at a point some distance from two or more point charges.
6. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric force on a charged particle placed in an electric field.
7. Sketch the electric field pattern in the region between charged objects.
8. Use Gauss's law to determine the magnitude of the electric field in problems where static electric charge is distributed on a surface which is simple and symmetrical.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)